Seriously! 19+ Truths About In The Long Run, Costs Are People Missed to Tell You.
In The Long Run, Costs Are | Unfortunately these phrases are still similar enough that you can use either in your example sentence, although the nuance changes depending which you use. In this manner, brief focused family interventions followed by preventative maintenance sessions may decrease inpatient care costs in the long run. That gives the firm opportunities it does not have there are thus no fixed costs. In the long run, the firms' fixed costs are greater than its variable costs. In the long run, you can change anything about your business, so all costs are variable.
In the long run, the firms' fixed costs are greater than its variable costs. Because of that all costs are variable too. But in the long run, the entrepreneur has before him a number of alternatives which includes the construction of various kinds. In the long run, you can change anything about your business, so all costs are variable. The firm has time to build a bigger factory and respond to changes in demand.
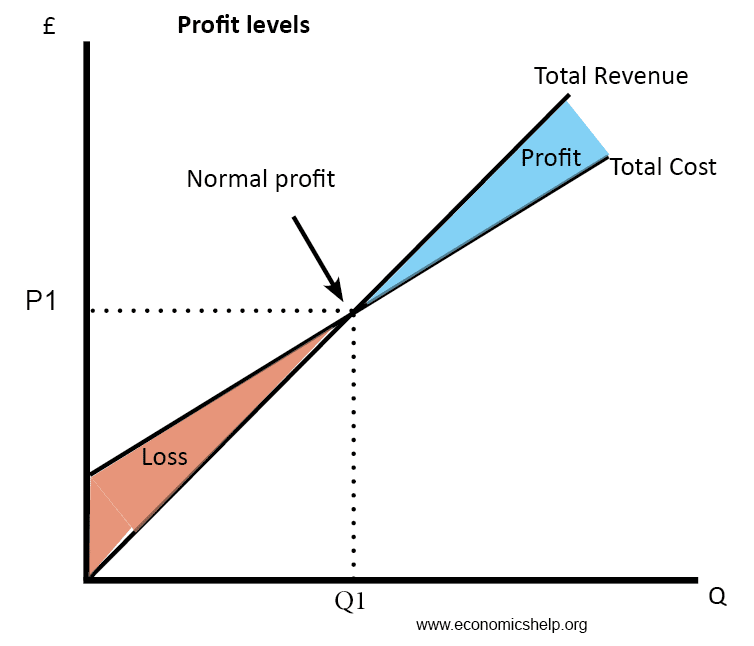
All costs are variable, so we do not distinguish between total variable cost and total cost in the long run: In the long run, the average cost curve is always downward sloping. The firm has time to build a bigger factory and respond to changes in demand. The lrac curve assumes that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix, as described in the previous section, for producing any level of output. Because all costs are variable, the structure of costs in the long run differs somewhat from what we saw in the short run. In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable. In contrast, economists often define the short run as the time horizon over which the scale of an operation is fixed and the only available there are no truly fixed costs in the long run since the firm is free to choose the scale of operation that determines the level at which the costs are fixed. The factors of production can be used in varying proportions to deal with an increased output. I cover two similar but different ideas: In principles of economics the envelope curve is used as an approximation of the long run average cost function in figure, there are series of short run average cost (ac) functions shown. The long run contrasts with the short run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. Definitions are from oxford dictionary. The long run is defined as a period in which all inputs are variable.
It is assumed that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix, for producing any level of output. Long run cost refers to the time period in which all factors of production are variable. In the longer run there are no fixed costs because businesses or organizations keep on making changes to suit the changing economic conditions. In the long run, the firms' fixed costs are greater than its variable costs. When all inputs are variable.

Unfortunately these phrases are still similar enough that you can use either in your example sentence, although the nuance changes depending which you use. Note an important relation between lmc and sac here. Because of that all costs are variable too. In principles of economics the envelope curve is used as an approximation of the long run average cost function in figure, there are series of short run average cost (ac) functions shown. In the long run all costs are variable and the scale of production can change (i.e. In the long run, the average cost curve is always downward sloping. The lmc curve is derived by the points of tangency between lac and sac. This pattern was illustrated earlier in figure 1. In the short‐run, some factors of production are fixed. Since whatever we were doing in the short run is an option, but other things previously impossible are now possible. When all inputs are variable. The long run is defined as a period in which all inputs are variable. Because all costs are variable, the structure of costs in the long run differs somewhat from what we saw in the short run.
In principles of economics the envelope curve is used as an approximation of the long run average cost function in figure, there are series of short run average cost (ac) functions shown. The lrac curve assumes that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix, as described in the previous section, for producing any level of output. Each such figure is arrived at by dividing change in total cost by change in output. But in the long run, the entrepreneur has before him a number of alternatives which includes the construction of various kinds. The long run contrasts with the short run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium.

In the long run, the factors of production may be utilised in changing proportions to produce a higher level of output. The u‐shape of the latc, depicted in figure , reflects the changing costs of production that the firm faces in the long‐run as it varies the level of its factors of production and hence the level of its output. That gives the firm opportunities it does not have there are thus no fixed costs. It is assumed that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix, for producing any level of output. In contrast, economists often define the short run as the time horizon over which the scale of an operation is fixed and the only available there are no truly fixed costs in the long run since the firm is free to choose the scale of operation that determines the level at which the costs are fixed. The factors of production can be used in varying proportions to deal with an increased output. When all inputs are variable. Because of that all costs are variable too. The firm has time to build a bigger factory and respond to changes in demand. Definitions are from oxford dictionary. These lower costs represent an improvement in productive efficiency and can give a business a competitive advantage in a market. In principles of economics the envelope curve is used as an approximation of the long run average cost function in figure, there are series of short run average cost (ac) functions shown. In this manner, brief focused family interventions followed by preventative maintenance sessions may decrease inpatient care costs in the long run.
In The Long Run, Costs Are: The factors of production can be used in varying proportions to deal with an increased output.
Source: In The Long Run, Costs Are
0 Response to "Seriously! 19+ Truths About In The Long Run, Costs Are People Missed to Tell You."
Post a Comment